|
|
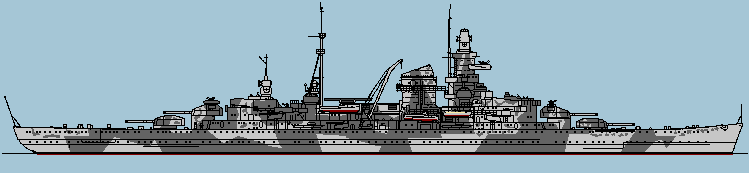
Schwerer Kreuzer Admiral Hipper
1944
|
|
History
Named after Admiral Fritz Ritter
von Hipper (1863-1932), commander of the reconnaissance forces
during the Battle of Jutland in 1916.
The heavy cruisers of the Kriegsmarine were a
result of the Washington Fleet Treaty of 1921, so called
"Washington Cruisers". Their displacement was not to
exceed 10.000 tons and their main artillery was limited to 8"
(20,3 cm) guns, but in reality they were up to 60% bigger than
allowed.
Between 1935 and 1937 the keels of five of this
ships were laid down which belonged to two slightly different
classes of ships: The Admiral Hipper and her sister Ship Blücher
, the improved second batch consisting of the Prinz Eugen ,
Seydlitz and Lützow . The last two were
originally planned to be big CLs with an armament of twelve 15 cm
guns, but due to the lack of guns and turrets and the threat of a
new class of Soviet cruisers, the ships were built as additional
ships of the Prinz Eugen design. Those ships were designed
with the idea of commerce war in mind, they should attack allied
merchant shipping and evade allied warships, but it soon got obvious
that they were not ideal for this task. With their high-pressure
steam engine their fuel consumption was too high and their
operational range was not big enough to be used in the North
Atlantic. In addition, the complicated engine construction often
broke down. Of the five ships, only three got completed at all.
The Admiral Hipper was destroyed by her
own crew in the final days of the war.
|
| Construction
Data |
Dimensions |
Commanders |
| Laid
down: |
Blohm
& Voß Hamburg, 06.07.1935 |
| Launched: |
06.02.1937 |
| Commissioned: |
29.04.1939 |
| Fate: |
blown
up 03.05.1945 (Kiel Shipyard) |
| Costs: |
85,8
Mio Reichsmark |
|
| Size
(Max): |
18200
t |
| Length
(Total): |
205,9
m |
| Length
(Waterline): |
|
| Beam: |
21,3
m |
| Draft: |
7,7
m |
| Crew: |
~1600 |
|
| KptzS
Hellmuth Heye: |
29.04.1939
- 03.09.1940 |
| KptzS
Wilhelm Meisel: |
04.09.1940
- 10.10.1942 |
| KptzS
Hans Hartmann: |
11.10.1942
- 16.02.1943 |
| KzS
Fritz Kraus: |
Feb.
1943 |
| KptzS
Hans Henigst: |
Mar
1944 - May 1945 |
|
|
Weapons |
Armour and
Aircraft |
Engines
& Performance |
| 20,3cm
SK (8"): |
8 |
| 10,5
cm L/65 C/33: |
12 |
| 4
cm Flak: |
6 |
| 3,7
cm L/83: |
8 |
| 2
cm MG L/64: |
32 |
| 53,3
cm Torpedoes: |
12 |
|
| Deck: |
12-50
mm |
| Belt: |
70-80
mm |
| Command
Tower: |
50
- 150 mm |
| Turrets: |
70
- 105 mm |
|
| Shafts: |
3 |
| Turbines: |
3 |
| Type: |
Blohm
& Voß |
| Total
Performance: |
132000
shp |
| Speed: |
32,5
kn |
| Range: |
8000
miles at 20 kn |
|
|
|
Operational
History
| March
1939: |
Final
Trials. |
| 29.04.1939: |
Commissioned. |
| June
- August 1939: |
Training
and trials. |
| July
1939: |
Training
voyage to Sweden and Estland. |
| August
1939: |
Patrols
in the Baltic Sea. |
| 06.11.1939-12.01.1940: |
Final
construction in Hamburg: New bow and funnel cap added. |
| January
1940: |
Trials
and training in the Baltic Sea. |
| 17.02.1940: |
Admiral
Hipper is put into active fleet
service. |
| 18.02.1940: |
Together
with BCs Scharnhorst , Gneisenau and several
destroyers, the Admiral Hipper operated between
Britain and Scandinavia to attack allied convoys. No enemy
ships were found during this operation. |
| 08.04.1940: |
Operation
"Weserübung":
Heading to Drontheim, Admiral Hipper and the
destroyers Bernd von Arnim and Hans Lüdemann
engaged the British destroyer Glowworm . The Glowworm
was sunk, but Admiral Hipper collided with the wreck. |
| 10.04.1940: |
After
landing troops in Drontheim, Admiral Hipper joins BCs
Scharnhorst , Gneisenau on their way back to
Germany. Although the British Home fleet is also operating in
the same area, both sides do not meet. |
| April
- June 1940: |
Repairs
in Wilhelmshaven. |
| 04.06.1940: |
Operation
"Juno"
Along with BCs Scharnhorst , Gneisenau and
the destroyers Karl Galster , Hans Lody , Erich
Steinbrinck and Hermann Schoemann , Admiral
Hipper raids the area of Hastad, Norway and sink
the troop transport Orama , the tanker Oil Pioneer
and the submarine hunter Juniper. |
| 20.06.1940: |
Admiral
Hipper and BC Gneisenau
start an operation against the British northern Patrol, but
the operation is canceled after Gneisenau is hit by
an torpedo the next day. |
| 25.07
- 09.08.1940: |
Operation
against allied merchant shipping in the Arctic sea, only
neutral ships are detected. |
| 12.08
- 07.09.1940: |
Repairs
in Wilhelmshaven. |
| 12.09
- 18.09.1940: |
Admiral
Hipper is planned to be used for support operation for
"Operation Seelöwe". |
| 30.09
- 28.10.1940: |
Repairs
in Hamburg after engine failure. |
| 01-27.12.1940: |
Operation
"Nordseetour":
First Atlantic mission: Attacks convoy WS5A about 700 miles
west of Cape Finestre and engages British CA Berwick
and DDs. Berwick and one merchant were severely
damaged, another merchant sunk. Admiral Hipper
returns to Brest, France. |
| 01.02
- 14.02.1941: |
Second
Atlantic Mission: On Feb. 11, Admiral Hipper attacks
the unprotected convoy SLS64 at 37°12'N, 21°20'W, sinking 7
of the 19 merchants and damaging several others. Due to fuel
shortage, Admiral Hipper has to return to Brest,
France. |
| 15-28.03.1941: |
Returns
to Kiel via the Denmark Street. |
| -
November 1941: |
Repairs
in Kiel, several water tanks are modified to oil tanks to
enlarge the operational radius. |
| 19.03.1942: |
Escorted
by the destroyers Z24 , Z26 , Z30
and the torpedo boats T15 , T16 and T17
, Admiral Hipper is sent to Drontheim, Norway. |
| 05.07.1942: |
Operation
"Rösselsprung":
Together with BB Tirpitz , CA Admiral Scheer
, escorted by the destroyers Karl Galster , Theodor
Riedel , Friedrich Ihn , Hans Lody
, Z24 , Z27 , Z28 , Z29 , Z30
and the torpedo boats T15 and T7, the Admiral
Hipper searches for the convoy PQ17 in the arctic sea.
Although no contact was made, two third of the convoy is
destroyed by U-boats and aircraft. |
| 10.09.1942: |
Admiral
Hipper , Admiral Scheer , the CL Köln
and several destroyers relocate to the Altafjord. |
| 24-28.09.1942: |
Along
with the destroyers Z23, Z28 , Z29 and Z30
, Admiral Hipper is doing the offensive mine
operation "Zarin" off the north west coast of Novaja
Semlija. |
| December
1942: |
Battle
in the Barents Sea:
Admiral Hipper , CA Lützow and the six
destroyers Richard Beitzen , Theodor Riedel
, Friedrich Eckoldt , Z24 , Z30 and
Z31 , attacks convoy JW51B at 73°N, 29°E. Hipper
sinks mine seeker Bramble and damages DD Achates
(which is later sunk) but the attack is aborted after
the British CL Sheffield and Jamaica archive
one hit on the Admiral Hipper . During the battle, in
which only one merchant is damaged, DD Friedrich Eckoldt
is sunk. |
| February
1943: |
After
provisorical repairs, the Admiral Hipper is sent back
to Germany via Drontheim. |
| 07.02.1943: |
Arrived
in Kiel. |
| 28.02.1943: |
Transferred
to Wilhelmshaven and put out of service. |
| 01.04.1943: |
Because
of the increasing air threats, Admiral Hipper is
town to Pillau. |
| 01.03
1944: |
Admiral
Hipper recommissioned. |
| Autumn
1944: |
Used
as a training ship. |
| 15.01.1945: |
Repairs
in Gotenhafen. |
| 30.01.1945: |
Admiral
Hipper leaves Gotenhafen with 1529
refugees on board following the passenger ship Wilhelm
Gustloff to Kiel. The Wilhlem Gustloff was
torpedoed by a Russian submarine, but Admiral Hipper
arrived at Kiel unharmed on 02.02. 1945. |
| 03.04.1945: |
Admiral
Hipper is hit by bombs during a
British air attack. The ship is heavily damaged. |
| 09.04.1945: |
Again
hit during an air attack, superstructures heavily damaged. |
| 03.05.1945: |
Blown
up in the dock of Deutsche Werke, Kiel. |
| 1948/49 |
Moved
to Heikendorf Bight and scraped by the British. |
|
| |
|

