|
|
Panzer PzKpfw Mk I (SdKfz 101) |
|
Panzer Mk I History
Origins
The PzKfw I had its origins in the design of the
Carden-Loyd machine-gun carrier, an example of which was obtained for
study during 1932. Five German firms submitted designs and the Krupp entry
was awarded the production contract. The Krupp entry was designated the
LKA I, but was given the cover name of La S, which stood for agricultural
tractor. Krupp was responsible for the hull and chassis, and Daimler-Benz
built the superstructure, but the first prototypes were built by Henschel
and delivered during December 1933.
Models
PzKfw I Ausf A
The first production variant was the Ausf A and 150 were
built by Henschel, starting in July 1934. Weight of the original PzKpfw I
was 5.4 tons. It differed from the LKA I prototype in having smaller road
wheels and an external beam supporting the suspension. Armour was 13 mm
thick, and armament was two 7.92 mm machine-guns mounted side-by-side in
the turret. The first Ausf A vehicles were delivered during 1935.
PzKpfw I Ausf B
The Ausf B formed the major type of the 1,500 PzKpfw Is
built. It was longer than the Ausf A due to the addition of an extra road
wheel to improve traction, and the engine was improved from a 60 hp model
to a 100 hp petrol engine. The armament and armour remained the same but
weight was increased to 5.8 tons. This was the variant which formed part
of the panzer divisions during the invasions of Poland and France, and a
few were left in service in 1941 when Russia was invaded.
In 1939, a proposal was made to develop the PzKpfw I as a small infantry
support tank. A few prototypes were built which featured thicker armour
and a redesigned suspension. On one design the twin machine-gunswere
replaced by a 20 mm cannon with a co-axial machine-gun, but the project
did not get beyond the prototype stage.
Variants
After 1940 the basic PzKpfw I was used as the basis for a series of
special vehicles. The main variants were as follows:
Kleiner Panzerbefehlswagen I (SdKfz 265)
On this variant the turret was replaced by a fixed box structure and the
result was used as a mobile command post. One machine-gun was fitted.
Flammpanzer I
These were Ausf A field conversions made in North Africa to give the
Afrika Korps a mobile flamethrower. Only a few were so converted.
PzKpfw I(A) Munitions-Schlepper (SdKfz
111)
This was a conversion of the Ausf A in which the turret and superstructure
were removed to enable the open hull to be used for carrying ammunition
for mobile columns.
15 cm sIG 33 auf Geschutzwagen I Ausf B
(see below)
Produced in 1939, this carried a modified infantry gun in a high open box.
It saw action in 1940 and 1941 but was withdrawn soon after as the gun was
really too heavy for the chassis. This was the first German self-propelled
gun.
Panzerjager I fur 4.7 cm Pak(t)
In order to give a degree of mobility to anti-tank units a number of Czech
guns were placed on Ausf B chassis behind a shield installed in place of
the turret. This variant became the first of the Panzerjager tank-hunting
vehicles which were later produced in a wide variety of types and
calibres. The PzJa'g I saw action in France and North Africa.
PzKpfw Ib Ladungswerfer 1
This was a specialised engineer vehicle used to carry demolition charges
on a movable gantry. Not many were so converted.
Gutted hulls were often used as tractors or for driver training.
Technical Specification

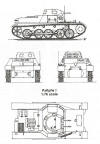

_small.jpg)

